AI’s a weird industry. So far almost no one is making any money, certainly not the major Western AI companies: Anthropic and OpenAI. Every query costs more than the revenue it generates. The primary beneficiary has been NVidia: they’re making money hand over fist, and suppliers of data centers and power have big customers in AI. But AI itself doesn’t make money. (Not Western, anyway. Deepseek, which is 20 to 30 times cheaper, probably is.
The energy required for Western AI is huge, and it’s mostly dirty energy. AI requires mostly 24/7 energy, which means renewables are out. It needs nuclear or carbon intensive sources like coal and natural gas and turbines. MIT did a massive dig into this in March.
The researchers were clear that adoption of AI and the accelerated server technologies that power it has been the primary force causing electricity demand from data centers to skyrocket after remaining stagnant for over a decade. Between 2024 and 2028, the share of US electricity going to data centers may triple, from its current 4.4% to 12%.
AI companies are also planning multi-gigawatt constructions abroad, including in Malaysia, which is becoming Southeast Asia’s data center hub. In May OpenAI announced a plan to support data-center buildouts abroad as part of a bid to “spread democratic AI.” Companies are taking a scattershot approach to getting there—inking deals for new nuclear plants, firing up old ones, and striking massive deals with utility companies.

AI’s a lot more intensive than traditional methods. For example, AI vs. a Google search (granted Google search sucks, but that’s because Google wants it to suck.)
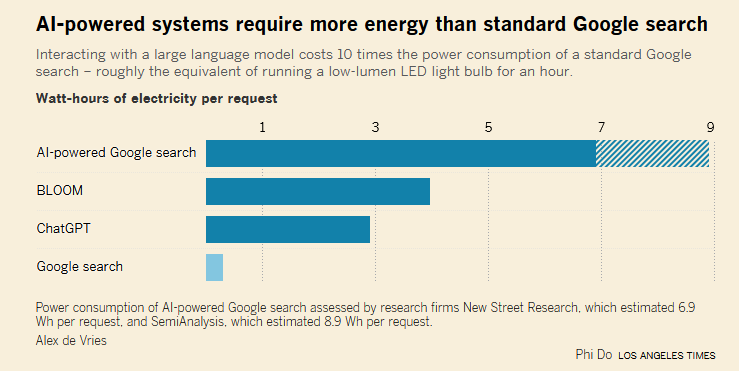
It’s long been noted that one of the biggest issues with climate change is that we can expect it to reduce the amount of fresh water available. AI gobbles that:
AI is also thirsty for water. ChatGPT gulps roughly a 16-ounce bottle in as few as 10 queries, calculates Shaolei Ren, associate professor of electrical and computer engineering at UC Riverside, and his colleagues.
ChatGPT 5 power consumption could be as much as eight times higher than GPT 4 — research institute estimates medium-sized GPT-5 response can consume up to 40 watt-hours of electricity
Whoa! That kind of puts paid to rising by 10% a year and other such assumptions. It doesn’t look like new models are scaling linearly.
We have a climate change problem already: lots of extreme weather, disrupted rainfall patterns and massive wildfires. The permafrost is bubbling and releasing methane and arctic temperatures are absurd (hitting 30 celcius in some cases).
Now if this tech was truly transformative, if it made everything so much better, maybe it would be worth it. But so far, with a few exceptions (mostly running thru millions of combinations to assist research) it seems like it’s better search, automatic image generation, a great way for students to cheat and may make programming faster. (There’s some dispute about this, one study found it made coders slower.) So far agents are duds, unable to even run a vending machine.
On the downside, even AI boosters claim it’s likely to put vast numbers of people out of work if it does work, wiping out entire fields of employment, including SFX, illustrators, artists, writers, customer service and perhaps most entry level jobs. We’re told AI has a small but existential risk of wiping out humanity. It gobbles water and energy and causes pollution.
What, exactly, are we expecting to get from AI (other than NVidia making profits) that is worth the costs of AI? Does it make sense to be rushing forward this fast, and in this way? Deepseek has shown AI doesn’t have to use so many resources, but Western AI companies are doing the opposite of reducing their resource draw. Eight times as much energy? How much more energy with GPT-6 use?
It seems like we’re unable to control our tech at all. This used to be the killer argument “well, there’s no controlling it, so why even try?”
But China’s AI uses way less energy. Apparently China can control it, and we can’t? So it’s not about “can’t”, it’s about “won’t”. Using less resources would mean less money sloshing around making various Tech-bros rich, I guess, and we can’t have that.
And all this for an industry where the primary actors, OpenAI and Anthropic aren’t even making money.
Perhaps we could be using these resources in a better way? China is spending their money on producing three-quarters of the world’s renewable energy, and ramping up nuclear power. Their carbon emissions are actually down. Their economy is growing far faster than ours. They’ve almost completely moved over to electric cars, they have high speed trains, and their space program is going gangbusters. All this while reducing rent by over a third in the past five years.
You don’t have to be an AI skeptic to think “maybe this is a misallocation of resources?” Is it really going to change everything so much so that it “makes America great again”? Is western AI so much better than Chinese to make that difference even if AI is as big a deal as its greatest boosters say?
Maybe the US and Europe should be concentrating on more than just AI? Not letting China continue to march ahead in almost every field, while putting almost all the marbles on one big project that they barely have a lead in anyway?
I don’t want to overstate this issue. The amount of energy and water used doesn’t come close to, say, expected increases in air conditioning. (Though if increases in draw continue to ramp up similar to GPT-5 we’ll see. And, the more energy we use, the more air conditioning we need thanks to fairly obvious feedback.) But still, what are we getting for it?
Just some things to think about.
***
If you’ve read this far, and you read a lot of this site’s articles, you might wish to Subscribe or donate. The site has over over 3,500 posts, and the site, and Ian, take money to run.

mago
Another symptom of a world gone mad. There’s no benefit from this technology, only destruction. The bus goes full speed over the cliff. I despair.
Like & Subscribe
It’s the beginning of a post-monetary world and what a world it will be. It cannot be judged any longer on its monetary merits for it is the precursor to a new world where monetary evaluation no longer holds sway.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9VAuC9Bi5UQ&t=382s
j
So far it’s just the standard Silicon Valley startup game. Expand fast, take market share, figure out the business model later.
Most startups never do figure out their business model, and run out of money sooner or later.
But the last big successful business (model) of Silicon Valley is Uber, and I think it’s a good case study here.
It’s no secret that Uber doesn’t have a business model in the traditional sense. They are nothing but a taxi company with a very expensive app on top of it, to the tune of $billions each quarter.. There’s no way that they could compete on the actual market.
But what Uber has going for it is dumping money. Last I heard they are profitable in three cities exactly, New York being the most famous of them. The play has been to undercut the competition until they all go bust, then rise prices. If some new competition arrives, rinse and repeat. The end result is that Uber is now the only game in New York, the service quality is half of what it used to be, the price is twice as expensive, and there’s no protection for customers, since it’s not even legally a taxi service.
As long as Uber has cash to keep this going, and as long as the municipalities are as clueless and corrupt as they are, this cancer will only grow. But they obviously cannot finance themselves on three cities only, so the cancer also has to grow.
This is probably how the AI game is going to run, too. Get everyone to fire their workers, then rise prices. And prices have to be raised. Even the high paying customers don’t pay for what the costs are, and paying users are only a fraction of total users. But get those paying users to fire their staff, and they will be locked in. Then they will have a choice – keep paying too much for low quality slop work from AI, probably still about 5% cheaper than labor, or go through the pain of building up a completely new workforce from scratch – and the more time passes, the less people on the job market will have any idea how to do the job at all.
Welcome to the future.
Feral Finster
Nobody of influence and authority cares about the consequences. Those are for the poors to deal with.
Found on internet:
“Agree completely that this is a hopeless unsustainable bubble. There may be small portions of current LLM investment that produces products people will freely pay for, but the magnitude of proposed spending cannot happen, and this will trash the stock market at some point.
But take another step back. This is not an MBA-type business/financial problem anymore. The real question is what happen after the stock market decline, and that is a political problem. As you and your readers understand after the dot-com crash and the 2008 crisis, there was widespread popular realization that the financial world had screwed over the rest of society royally, but none of the people who most directly “caused” those crises were punished, and the broader bad behavior quickly resumed.
An AI crash would be a much bigger deal politically. Both political parties are totally beholden to not only “big tech” but the broader “number go up” ideology where the artificial inflation of the equities of a handful of companies is falsely equated with widespread economic growth. Every one of Trump’s signature programs (huge tax cuts, huge spending on immigration and defense) falls apart if those big tech stock prices collapse, along with the idea that he could serve both his big donors while protecting non-wealthy MAGA supporters. National Democrats are equally devoted to big tech and unlimited defense spending, and if the numbers stop going up the wealth of the Democrats core PMC supporters will crash.
Financial/donor interests controlled both parties in 2008 but issues like CDOs could be isolated and portrayed as one-time anomalies that didn’t fundamentally challeng “number go up” thinking. Housing was still a “real” thing but “AI” isn’t and a 2026 bust would create an existential challenge to “number go up”
If the Dow Jones collapses absolutely every political faction with any real power will fight tooth and nail to deny it is happening, to shovel massive taxpayer funds to help prop up Wall Street and Big Tech and to furiously oppose anyone demanding real changes or demanding that those factions pay a price for the destruction they unleashed.
There are thousands of people like you who have been pointing out the growing problems for years, but they have zero voice within either party and after decades in the wilderness there is no realistic possibility they could suddenly organize. Big Tech has a well developed playbook for strengthening their already massive dominance. See “Super PAC aims to drown out AI critics in midterms, with $100M and counting” (Washington Post 26 Aug).
“Might the AI stock bubble burst?” is no longer a critical question. “What will all the political factions that were cheerleaders for Number-Go-Up do after it bursts” is a much more important question.
And my response:
“If the Dow Jones collapses absolutely every political faction with any real power will fight tooth and nail to deny it is happening, to shovel massive taxpayer funds to help prop up Wall Street and Big Tech and to furiously oppose anyone demanding real changes or demanding that those factions pay a price for the destruction they unleashed.”
Of course. Were the AI bubble to burst, Team D and Team R alike would, on the one hand frantically point the finger at the other Team, and at the same time, they would be shoveling as much money as it takes to make sure that no billionaire had to miss a payment on his next yacht.
The peons don’t matter, not as consumers of AI or even as cogs to be replaced.
Oakchair
The oligarchs fear the same thing they need. People and workers. They need the workers and people in order to extract their labor. They fear those people will eventually decide to overthrow their psychopathic masters.
One solution to this paradox is to replace workers and people with Robots/”AI” and then get the “useless eaters” to go the way of the Dodo.
Purple Library Guy
Uber is actually a bad comparison. So first, Uber is profitable now, after a long time of not being profitable. And, Uber is profitable in EXACTLY the way everyone who looked at them realistically always knew they were going to be. Uber’s business model was ALWAYS to run competitors out of business with rates too cheap for those competitors to match, and then jack prices up once they had a monopoly. The playbook worked in many places, Uber now has many local monopolies, so they’ve jacked prices up and started making money. Really, the app was almost beside the point, except in the sense that it allowed them to sidestep tons of local regulations around taxis by claiming not to be a taxi company. Well, and allowed them to screw the drivers real hard.
But that playbook, you’ll notice, requires a product that people already want and ideally sort of need. Uber is a taxi company with an app; people already use taxis, and sometimes kind of need them. There is a market to corner which you can gain money from being the monopolist of.
AI has no product. It has some sort-of-maybe products, but they don’t work and it’s unclear how much use most of them would be if they did; none of them are worth what they cost. In some cases they are maybe worth the prices the big AI companies are charging (although probably not), but the big AI companies are losing money with every query because nobody would pay what it really costs. There is no market to corner.
It’s not just the top two companies who aren’t making money on AI. NOBODY is making money on AI (except NVidia, who aren’t using it). All the little startups trying to use AI to do stuff, make AI into products . . . NONE of them are making money. By all accounts the big boys who aren’t AI companies as such but have AI and are sinking big money into it (e.g. Google, Microsoft), are also losing a ton of money on AI. Meanwhile, GPT-5, for all the effort put into it, and for all the extra energy and computing power poured into each query, by all accounts performs barely better than GPT-4 and in some cases worse. I’ve been saying for a while that I thought Large Language Models were a more mature technology than people thought and had reached a point of diminishing returns; I was righter than I knew, apparently.
The big question right now is not, will AI succeed. I mean, I suppose it might, but the chances seem really, really low at this point. The big questions are things like, how long before the bubble bursts, and what happens when it does?
I am fairly confident that 5 years from now, LLM AI will be mostly open source models related to Deepseek and other Chinese ones. And, the biggest use will be for virtual girlfriends who will “do” kinky sex stuff frustrated guys can’t find real girls to do (and maybe virtual boyfriends who will “do” emotional support frustrated women can’t find real guys to do because too many of the guys are incel jerks). All the job replacement stuff will disappear, most of the coding stuff will go away, most of the companies will go under. Probably this will trigger a recession everywhere that the government isn’t willing to do Keynesian stimulus, which would be most of “the West”.
Flaser
I’m working for a big telecom company, supplying equipment for mobile network operators (e.g. Verizon, AT&T).
From what I’ve seen, most successful uses of AI in my field is classic machine learning: optimization problems, finding the best configuration of the system, etc. Most importantly: these are not large language models. The use of these happens in a wide range of applications.
We also have some neural-net based stuff, but the training data, the deployment costs and so on are a far cry from the current craze of “LLM AI” that grips a lot of tech. (These agents suggest optimal network configuration to operators based on observed network traffic trends).
With a handful of exceptions, (e.g. network configurator) these solutions are quietly deployed in the background, bringing tangible, but not revolutionary improvements to these systems.
By contrast, management is in the grip of the LLM craze, especially the promise of coding assistance AI.
So far my experience was that, while some people find them useful, they failed to deliver on the promises of truly better productivity. This is in with this oft-quoted study:
https://www.theregister.com/2025/07/11/ai_code_tools_slow_down/
j
But AI does have a product. It’s just that you and me are not the customers.
And let’s clarify here that by AI we mean LLM, because that’s what the bubble is about.
The product of AI is the promise to all the bosses in the world – you can fire your workers. You can run your business without the expenses of the payroll, and without the mess of having to deal with people, both of employees, and of customers.
This is catnip to every C suite executive in the world. None of them care if the quality of their own product goes down, or if their customer relations suffer. All they want is their product to be tolerable enough that their customers don’t walk off en masse.
And in this AI is a product that people want and need. Twisted wants and needs, but real nevertheless, and the way we organize our society, these wants and needs will have it their way. Customer support all over the world is more and more run by AI already. News articles are written by AI, half of youtube is AI, more and more of programming is just vibes – and nobody is walking away yet. The slop must flow, and everything must turn to crap.
All the AI executives need is that their own product be tolerable enough that their C suite customers don’t walk off en masse.
What the impact to the economy or society will be, we’ll see soon enough, but it won’t be anything pretty.
Joan
For those who use duckduckgo, you can use noai.duckduckgo.com to search without search assist and duck.ai, and to have ai-generated images removed from image searches.
If you want to opt out manually here is an explanation on how to do that:
https://duckduckgo.com/duckduckgo-help-pages/ai-features/opting-out-of-ai
On another note, AI has changed the way I communicate with my husband. I don’t ask him anything anymore; I just google it myself because my husband doesn’t answer questions anymore, only Claude does.
Purple Library Guy
Yeah, but j, LLM AI doesn’t actually deliver that. It gives people fantasies that they could get that, but in most businesses where crappy text isn’t the actual product, using the stuff to replace people won’t actually get you poor-but-tolerable quality, it will get you nothing. I’m sure there will be enthusiastic CEOs who bet the farm on replacing all their employees with AI; they will lose the farm. Replacing employees requires “agents” to work, and they don’t.
(AI might be able to replace managers murfling in meetings, but that’s not who they’re trying to replace)
j
My point is AI replacing workers is not some theoretical future thing, it’s already happening all around us. I gave you examples of fields where this is very real. I’ll add to that delivery bots and robotaxis for good measure, which you will find roaming in your nearest city big enough. Ukraine is now starting to field AI drone swarms, Israel is creating artillery targets in Gaza using AI because human beings cannot possibly create enough of them fast enough.
Maybe we have different definitions of an AI agent “working”… I am in no way implying that the work, or “work” for that matter, is anything but crap. But that crap is good enough for our masters, and that’s all that matters for now. They’re not the ones that have to eat it.
Whether that crap is good enough for us, so that the businesses employing AI agents might stay afloat long term, that’s another matter, and as of yet undecided. With regards to at least news, media, and culture, we have been consuming utter crap already for decades, I’m not seeing AI making it any worse than what it already is. And can Comcast customer support become any worse, either? We put up with it because there’s no alternative, barring pitchforks.
I would very much hope that our AI overlords lose the farm, but I’m not getting my hopes up. I’m betting more on the pitchforks, as more and more of the general populace finds itself out of work.
Purple Library Guy
I thought the topic was Large Language Model “AI”. Robotaxis don’t use that. I really doubt drone swarms do either. Computer software in the broader sense is replacing jobs, yes. It’s a long, gradual process that has been going on for decades and does not seem to have impacted employment rates, presumably because other jobs get created.
Customer service can be AI because for big corporations, customer service failing to work while appearing to be there is the OBJECTIVE. The other examples you mentioned are what I had already described as “businesses where crappy text is the actual product”. Although either “half of Youtube” is a vast exaggeration, or I’m experiencing all the wrong bits of Youtube . . . which is possible, because I’m quite picky. But the thing is, there are not many such businesses. They don’t represent very much employment. The number of journalists AI could potentially replace is far smaller than the number of journalists that have already lost their jobs from media consolidation–there’s like a quarter as many journalist jobs as there were in 1990, and hardly anyone even bloody noticed. And for anything where workers have to do things . . . not even REAL things, just, things, make very minor decisions and act on them . . . AI just simply can’t do those jobs. It’s not that it can’t do them well, it just can’t do them. As to the programming . . . as far as I can tell, if you sack half your programmers and tell them to use AI to increase their productivity, you will end up with half as much software product produced . . . or less. Companies can hype vaporware for a while, but eventually you have to sell something. Pretending to have AI produce software may currently get you some venture capital, but it will not get you software to sell. I don’t think LLM AI in programming is going to end up being a very big thing. And it’ll be a smaller thing after the AI companies go under, because even if there’s that one crank in every office that swears the stuff increases their productivity and wants to use it, if the AI companies no longer exist to sell it to them, the office won’t be buying it for them. If it was free, maybe . . . but queries cost money.
It’s a bubble. Its functions are not valuable enough for most of the current customers to be willing or able to pay what it actually costs on a long term basis. Current prices are a sort of extended teaser, like with Uber. Unlike with Uber, there is no monopoly available to let them jack the prices up . . . at the REAL price, human labour becomes a better deal again. OpenAI et al’s only hope was for the costs to come down to where they could make money charging the little that the traffic would actually bear for a low-value service. But their costs are instead going UP. It’s a bubble. It will mostly go away.
Forecasting Intelligence
Great post Ian.
I share your thinking on this.
StewartM
But China’s AI uses way less energy. Apparently China can control it, and we can’t? So it’s not about “can’t”, it’s about “won’t”.
I am reminded by a Youtube put out by Military History Visualized (two Germans) on German tank production. Turns they say out the biggest reason why German WWII tanks were “overengineed”, costly, and unreliable was—ta-da!–making them this way meant bigger profits for German manufacturers. Even though by this time in the war, Germany is losing, ripping the German government off for higher profits trumped any national good.
(So much for the Nazis being “socialists”, eh?)
In a related vein, the Ukrainians have been shelving the western tanks they have received: Abrahms, Leopards, and Challenger 2s–to re-field the supposedly laughable and mockable T-72s. Some of the same complaints about German WWII tanks are being made about Western ones: fuel-hungry, needs too much infrastructure and support, etc. Seems like the US forgot everything it knew from WWII how the ideal weapon must be able to fight in the field where sometimes you don’t have everything at-hand.
different clue
What do we call the various AIs which are not LLM AI? Single-focus AI? Special purpose AI? What?
Anyway, here is a little news videobit about how an ” Obedience to Standards Police AI” is cancelling users, including serious small-scale users, out of Instagram. And Meta has been very careful to have precisely zero humans in the complaints-department to take complaints and requests for re-instatement about this. It is titled:
” News 6 meteorologist blocked from posting hurricane updates on Instagram ”
Here is the link.
https://www.reddit.com/r/videos/comments/1nabz67/news_6_meteorologist_blocked_from_posting/