So a *European* startup called IB2 announced *in the US* the invention of an amazing new technology to upgrade low-grade bauxite – previously discarded as waste – into high-grade, which makes it usable to make aluminum and extract critical minerals like gallium, lithium, and rare earths in the process.
In the current context you’d think either Europe or the US would be all over it, right? Wrong. Somehow the first facility that startup ended up building is in Shanxi, China – built in 10 months flat (which, as you can guess, is almost impossibly fast)…
…How? Why? Speed and efficiency. According to the founder and CEO of IB2, Romain Girbal, they received “massive support” from the Shanxi government and were able to move at insane speed. As he puts it: “You could never go that quick anywhere else in the world – only in China. It is unique.”
And no, they didn’t do it by trampling on environmental regulations which, contrary to popular belief, are now actually quite drastic in China. As Girbal puts it: “Building a unit in China is very regulated – environmental and dangerous materials [are subject to] heavier regulation. Of course we followed everything but we had the support from the Shanxi province to help us move forward. Sometimes, being a foreign company, things can be slow with communication issues. When there were sometimes slowdowns, they were here to help and to push.”
The difference here is simple. China has regulations, and the government helps companies meet them. The government wanted this facility so they helped WITHOUT breaking the laws. Here in the West, we’d give them a tax break, and maybe we’d say “it’s OK to break the law this time.” That’s not what Shanxi did.
I am reminded of how US tax authorities built an auto-filing system which filled out tax forms for people, and helped them thru the process where it couldn’t fill them out. Unfortunately there’s a big business doing that already, so Congress, this year, forced the IRS to shut it down.
What the IRS was doing is helping people obey the law, but that threatened TurboTax’s profits, so…
This is how the Russians were able to ramp up weapons production so fast (or part of it.) They made it a priority and the government helped firms.
Safety and environmental regulations exist for good reasons. Most firms will cut every corner they can to make a profit, and those few with ethics will lose to those who say “who cares how many kids die of asthma due to pollution?”
BUT a properly run government doesn’t just make regulations, it helps firms meet those regulations. They aren’t, or shouldn’t be, meant to slow things down, but to make sure corners aren’t cut which will hurt consumers, workers or just the general population.
In most of the West regulators exist to say “no” and to ask for another report. They don’t much care if the business succeeds or not. In China (and, actually, in America before 1980 or so) governments want business to succeed so they help, but they also don’t want businesses to shove their negative externalities onto workers or citizens, so they also make sure they can meet the regulations intended to protect people.
As we’ve noted before, the US couldn’t do this if it wanted to, because contrary to propaganda, the US doesn’t have a ton of federal bureaucrats:
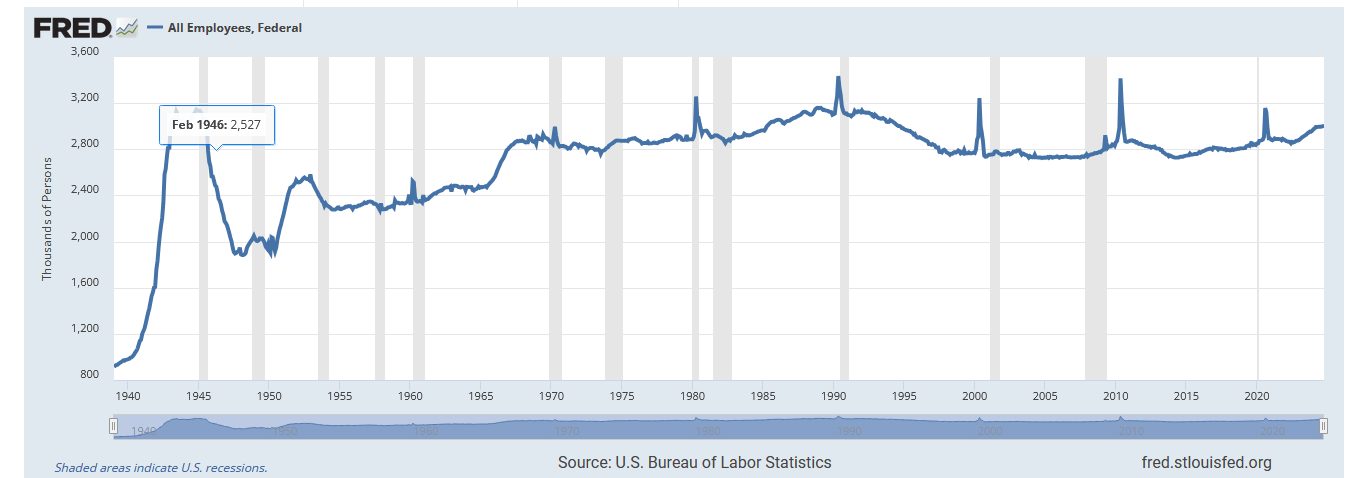
When you consider how much the American population has grown, you can see that the number of bureaucrats per capita has actually dropped significantly. In 1970 (which had about the same number of federal workers) the population was 205 million. Today it is 343 million. Most of that has been outsourced to contractors. Contractors who, of course, cost more than just doing it in house.
A friend of mine is in his early 80s, and he once told me how after Reagan came into office, the local Small Business Administration office, which had been very helpful to him in running his small accountancy business, got rid of half its employees and those who remained were no longer allowed to help as much.
Properly run nations want business to succeed and help them, but they don’t do it by letting them dodge regulations or cutting them for them, they help them by guiding them thru the process of meeting the regulations, and provide other aid as necessary to get the business going.
Once that was us. No more.
This site is only viable due to reader donations. If you value it and can, please subscribe or donate.

 It is now over 20 years ago that I first wrote that Israel would either become a single, secular state, or it would ethnically cleanse or genocide the Palestinian. There were no other solution sets: the land is not actually large enough, nor does it have enough water to divide it into two states and in any case, it was obvious Israelis would never go for that.
It is now over 20 years ago that I first wrote that Israel would either become a single, secular state, or it would ethnically cleanse or genocide the Palestinian. There were no other solution sets: the land is not actually large enough, nor does it have enough water to divide it into two states and in any case, it was obvious Israelis would never go for that.
While reading deeper, I found something much more important: a lot of these new humanoid startups aren’t building from scratch. Instead, they’re standing on the Unitree G1 frame and layering their own proprietary AI on top. That means Unitree has quietly become the default hardware platform for China’s humanoid boom — like the Android of robot bodies.
A few examples:
1. A-Bots Robotics (Shenzhen, 2024)
• Focus: precision assembly, modular SDK
• AI layer: Baidu Ernie-ViLM for object manipulation
• Notes: 150+ units in Foxconn trials; ~$22k package; tuned for fragile electronics
2. HPDrones Tech (Guangzhou, 2023)
• Focus: warehouse logistics + drone hand-off automation
• AI layer: proprietary SLAM + multi-floor routing
• Notes: partnered with Unitree; 500-unit rollout for e-commerce warehouses in Q1 2026
3. LeRobot Labs (Beijing, 2024)
• Focus: open-source robotics + reinforcement learning
• AI layer: embodied datasets, tool-use improvisation
• Notes: hacked 20+ G1s for universities; GitHub repo exploded; expanding to eldercare
4. Weston Intelligence (Hangzhou, 2023)
• Focus: healthcare — vitals scanning, bedside conversations
• AI layer: Tencent Hunyuan conversational model
• Notes: deployed in Shanghai hospitals; sub-$20k price; measurable patient-compliance benefits
5. DexAI Dynamics (Shenzhen, 2024)
• Focus: dexterity — folding fabric, micro-adjustments, teleop self-supervision
• Notes: $80M raised; 100 units deployed in garment factories; arguably the best hands in China now
And then there’s MindOn — the one that caught my eye earlier — using the G1 frame to build a full butler/housekeeping robot (“MindOne”). One of their engineers even said they eventually want their own frame, but that’s the point: everyone is starting on Unitree first.
Unitree has locked down the humanoid robot ecosystem
All these startups — even if they eventually design their own skeletons — are still tying their early models to:
• Unitree’s frames
• Unitree’s actuator supply chain
• Unitree’s low-cost motor ecosystem
• Unitree’s software layer and APIs
Once you build your first few generations on someone else’s chassis + firmware, you’re effectively locked into their ecosystem. Switching costs explode. You’d have to rewrite half your AI stack.
So Unitree has already achieved what Western robotics companies wish they could do:
Become the default hardware substrate for an entire national robotics industry.
This is exactly how China overtook the West in EVs — standardized hardware, cheap mass manufacturing, and dozens of startups building on top of the same base.
Unitree is still a private company.
Given everything above, the most obvious question becomes: When does Unitree IPO?
On 15–16 November 2025 (literally this weekend), Unitree completed its pre-IPO regulatory tutoring with CITIC Securities — an unusually fast four-month process that normally takes 6–12 months.
The company publicly stated in September that it expects to submit the formal prospectus and listing application to the Shanghai STAR Market between October and December 2025.
Market sources still quote a targeted valuation of up to US$7 billion (≈50 billion RMB).
Once the prospectus is accepted (usually 2–4 rounds of CSRC questions), the actual listing can happen remarkably quickly in a hot sector — sometimes inside 3–6 months. A Q1/Q2 2026 listing is the base case, but a very late-2025 listing is still possible if the regulator fast-tracks it the way they have the tutoring.
What About America?
Meanwhile… America’s Great White Hope Elon Musk is already behind.
Elon Musk promised that the U.S. would lead the humanoid robot race with Tesla Optimus — but the timelines have slipped, and the window has basically closed. By the time Musk’s robot is actually ready for real-world deployment — 2 years from now? 3? — China’s robotics companies will already be deep into mass production, with tens of thousands of units deployed across factories, warehouses, homes, hospitals, and service industries.
And let’s be real — we all already know this:
Tesla will NOT be cost-competitive. Not even close.
China has already hit the sub–$20k price point for serious humanoids. Several G1-derived platforms will likely break below $15k. Meanwhile, Tesla Optimus — if it gets out of prototype limbo — will land somewhere between $20k–$40k+, before customization, localization, or integration costs. It’s the exact same pattern we saw with EVs, solar panels, drones, lithium batteries, telecom gear — the U.S. builds one expensive proof-of-concept; China builds ten factories and ships globally.
So yes, Tesla’s robot may survive inside the U.S., but only through:
• tariffs,
• import bans,
• national-security excuses,
and whatever industrial-policy tool Washington can wield.
It won’t survive on merit. It will survive on protectionism.
But step outside the U.S.?
Why would any ASEAN, Middle Eastern, African, or Latin American country buy a Tesla robot when Unitree, UBTech, XPeng, and others are offering machines that are:
• cheaper,
• and available now — not in 2027,
• generations ahead and more advanced by 2027.
You think Indonesia, Malaysia, Brazil, Mexico, Turkey, or Saudi Arabia is going to pay double the price for a worse robot just to keep Washington happy? You think they’re going to turn down a $12k Unitree or $16k UBTech because Trump tries to bully them into paying for a $35k American robot instead?
The U.S. will absolutely try to pressure, coerce, or outright threaten developing countries into “buying American” — the same way it pressures them on telecom, semiconductors, energy infrastructure, ports, and industrial policy. But this time I don’t think most countries will obey.
They have options now.
By the time the U.S. finally ships its first commercially deployable humanoids in 2–3 years, the rest of the world will already be locked into the Chinese robotic ecosystem — Unitree frames, Chinese actuators, Chinese SDKs, Chinese AI integration, Chinese supply chains.
The EU, Australia, Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan — effectively U.S. satellites — may follow Washington’s orders and switch to American robots. Maybe. If their economies in two years can still afford it.
Everyone else?
Forget it.
Forcing U.S. factories and businesses to buy “American-only” humanoid robots — which will be more expensive and less advanced — will cripple U.S. competitiveness across the board.
If American companies are stuck paying $30k–$40k per unit for less capable Tesla or U.S.-made robots, while factories in China, Malaysia, Indonesia, Brazil, Vietnam, Mexico, Turkey, and everywhere across the Global South are deploying $12k–$18k Chinese robots at scale, the cost gap between U.S. and foreign manufacturing will explode. And it won’t stop at robotics — it will cascade downstream into every single sector that depends on automation:
• logistics
• warehousing
• construction
• agriculture
• textiles
• electronics assembly
• packaging
• even retail, service, and hospitality
If U.S. firms are locked into a high-cost, low-capability robotic ecosystem while the rest of the world uses cheaper, better, faster machines, then every American industry that relies on automation gets structurally handicapped. That’s not just a disadvantage — that’s YUGE and permanent.
So Trump’s protectionism will actually accelerate the decline of U.S. manufacturing competitiveness. Because the battlefield is no longer labor cost — the battlefield is automation cost.
And China will win that fight by orders of magnitude.
This is also why I doubt even America’s closest aligned countries will follow U.S. orders when Washington eventually demands they drop Chinese robots and buy American ones. Unless they’ve developed a death wish for their own industries, they simply can’t afford to sabotage themselves like that — especially when their economies will likely be in even worse shape two years from now.
Except Europe. Europe will probably obey, because their heads are shoved so far up America’s arse they can’t even think straight — and then there’s that incessant, obnoxious demand of theirs: “You must stop be friend with Russia first or we won’t play with you!”
In my opinion China will eventually move toward some form of universal income or redistribution. Once robots replace most human labor, the state will simply “tax” robotic productivity — in whatever form it chooses — and channel that output back to the population. China can do that because the government actually has the authority, the ideology, and the political structure to redistribute.
After all, that’s the logical endgame of communism, isn’t it? A fully automated productive base supporting human welfare.
America? No such luck.
In the U.S., the elites — the top 5%, or really the top 1% — will own the robots. They’ll own the factories, the logistics chains, the land, the means of production, and the automated labor force. Everyone else below them will get… nothing. No jobs, no prospects, no future, nada. Just a growing underclass structurally locked out of the new automated economy, where human labor is obsolete and redundant.
And unlike China, the U.S. government can’t — and won’t — redistribute. It won’t tax robots because it won’t tax the ultra-rich. It won’t implement a universal income. It won’t structurally rebalance anything. The millions displaced by automation will simply be left to rot — not because the technology is bad, but because the political system is incapable of adapting to it.
And if there’s one thing I’ve learned comparing Americans and Chinese: Americans are astonishingly ideologically rigid, stubbornly wedded to outdated principles even when reality punishes them. The Chinese, by contrast, are pragmatic — willing to bend, adapt, and change. That adaptability will matter a lot when robots replace human labor and make capitalism, as we know it, obsolete.
That’s why America is panicking. They know they can’t adapt.
Ian Comments: again, China is ahead in most technologies and they have an unparalleled ability to scale. Once they scale, no one else can compete. You either find a place where you’re ahead and concentrate on staying ahead, or you find a niche. It used to be that China didn’t feel the need to be ahead in everything, but Trump, in his first time, with his sanctions, changed that. The Chinese realized they had to own full stack of everything.
One side effect of this is that Musk isn’t going to get his one trillion dollar payday. It’s based on him hitting targets, including in humanoid robots which he won’t be able to make, because Tesla’s too far behind and lacks the ability to scale.
More on the transition away from labor-distribution capitalism soon.
And great piece by KT. Thanks for letting me post it.