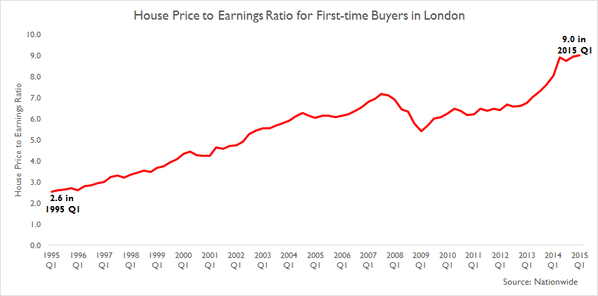
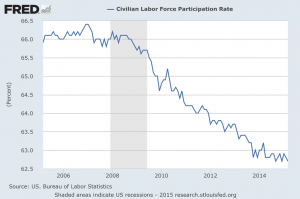
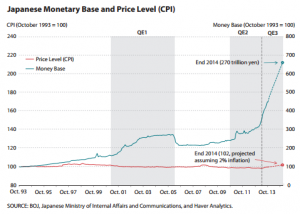
My parents were rich, then poor, then middle class during my life. My father both made and lost a fortune in his thirties and forties. I went to an elite private school, paid for partially by the UN. Then, I spent my twenties poor, often ill, and, on occasion, was only saved from the street by the kindness of friends.
When I think of class issues, I think of them in terms of corridors. In every gleaming office tower, they are there, in every upscale marble, glass, and steel mall—they are there. They are dark concrete, engrimed, lit by harsh fluorescent lights behind steel cages, streaked with the residue of years of waste. They are the corridors that the service staff use: the maintenance staff, the cleaners, the truck drivers, the blue collar guys who cart the heavy boxes and fixtures around. They are ugly, and often they stink.
The most disgusting set of corridors I ever encountered was in the Chateau Laurier. For those who don’t know, the Chateau Laurier is an old hotel connected by tunnels to Parliament Hill in Ottawa itself. It is one of the hearts of power in Canada. And the sub-basement has a smell that is something between rotten meat and acrid cheese with something acid and chemical cutting through it. I quite literally gagged the day I delivered food meant for the gullets of the rich to the old majestic Chateau, that magnificent palace whose opulent restaurants are but feet from a stench laid down for decades.
It’s that squalor that underlies the worlds of both opulence and sterility–the opulence of the upper class, the sterility of the middle classes’ office buildings. It’s those corridors in which those who earn little more, and sometimes less, than minimum wage work. For Lord save the clean, little people–in their white shirts and ties, their buffed oxfords, and their clean fingernails–save them from seeing the people who do the work that keeps their white walled world clean and running, the people who keep the air conditioning and the heat on, the carpets clean, and the light fixtures working.
The trolls come out at night as the offices empty. Once the daytime denizens are gone, they come scurrying out from their tunnels and are allowed to move through the offices; so as not to offend the others with the sight of their sweating for a living or dealing with dirt and garbage. And when the daytime denizens do see you, if you are one of those night-time trolls, they don’t see you. Their eyes don’t track you, they move right over you as if you were a piece of moving furniture—an appliance. They will only approach reluctantly if they need something. After they’ve gotten what they wanted, whacked the machinery, as it were, you usually find you’ve gone back to being an invisible appliance with whom eye contact is to be avoided at all costs. And you are paid in scraps. For your labor, you receive a pittance compared to those whose fingernails are clean, whose work involves the strain of typing on a keyboard, attending meetings, and picking up the phone.
That’s my second world, that world of tunnels. It’s a world I inhabit no longer, but it’s a world that haunts me, that I know exists alongside the antiseptic office world. Those corridor dwellers are the ones whose labor makes that new, office world possible—they are the trolls of the modern world, who come out at night, or who scurry through tunnels in the day, never to be seen by those whom their work supports. If seen, they must be ignored.
And they are.
And so I listen to John Edwards and I marvel that he dares speak of the unspeakable, of the great fear—not just of the middle class, but of all Americans. For we choose not to look at that which we fear. It’s not that we fear the working poor, or their humbler cousins, the broken, those who don’t even have job, much less a bad job. What we fear in them is that we might see people like ourselves.
For, to feel secure, in our beautiful world, we must believe that there is something fundamental that makes us different from the poor and the broken. We must think, “Ah, but I’m smarter,” or “I work much harder,” or, less gratifying but still good, “I have a better eduation than they do.”
We must think, then, “I am more valuable than them, I am different, what happened to them could never happen to me! I’m different! I am!”
We cannot see them as humans like us. That many of them work hard, or worked hard when they were allowed to. That most are not stupid, and that many are no worse educated than we. (And isn’t that the easiest thing to fix anyway? As though if everyone had a high school diploma, or a B.A., or a Ph.D., there would be jobs for them all.)
But I worked among them, lived among them, was one of them, and I know they work as hard, indeed harder, than most of the soft office workers whose lives they make easy. And I remember the screams from the soft, pampered bewildered sots when something went wrong in their pristine worlds and their inability to pick up a heavy box, or use a plunger on a toilet, or confront someone violent. Oh, yes, they disdained the goblins, but they’d coming running for our help fast rather than soil those soft hands.
And yes, this sounds bitter. And yes, it is. And yet, I’ve long moved on from that world. My hands are the soft ones now, I’ve not picked up a shovel in over a decade.
But I don’t think that what I do is somehow innately more deserving than someone who cleans toilets for a living, or who sits at a security desk and patrols to make people safe, or who digs ditches, or who… but why go on, make your own list of the underpaid and under-appreciated.
And so I listen to John Edwards and I know why he lost twice. People don’t like you when you make them look at the other side, at the dark fate that may await them one day if they’re a little unlucky; if their company downsizes, if they’re 45 and the company wants a youngster, or if some guy in China is willing to do their job for one-tenth the wage.
Like the way the middle class says about death “she passed away,” we don’t want to look firmly in the face of poverty and see that the face is our face, that its fate echoes ours. If seen, it must be ignored.
Mustn’t it?
(A Reprint, and now kicked back to the top from 2010 re-publication.)
If you enjoyed this article, and want me to write more, please DONATE or SUBSCRIBE.