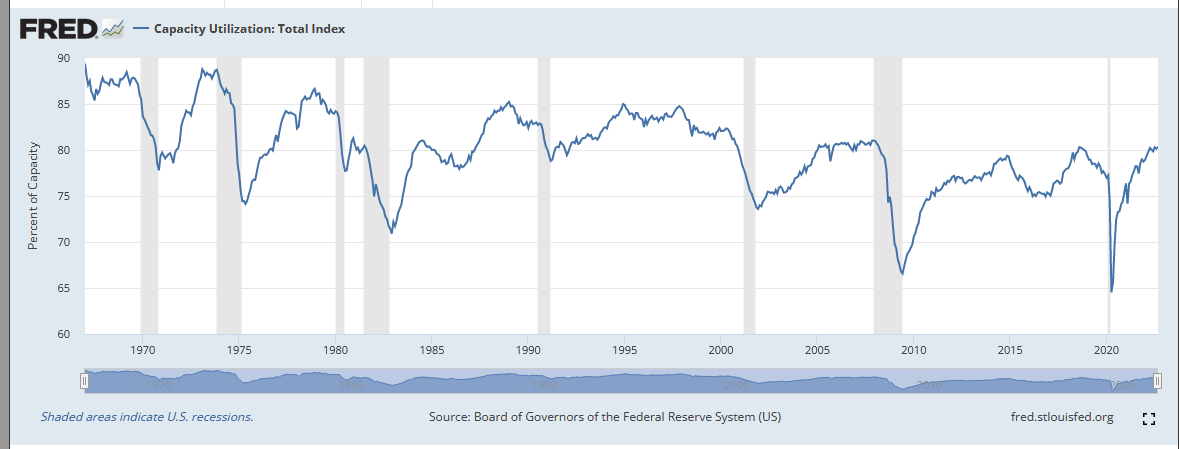
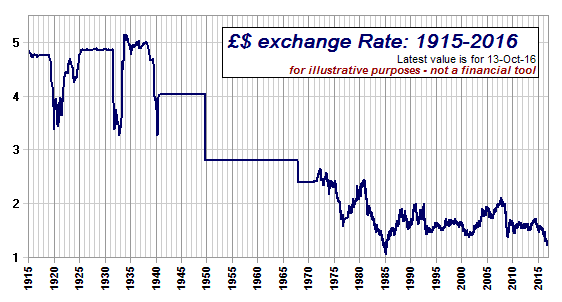
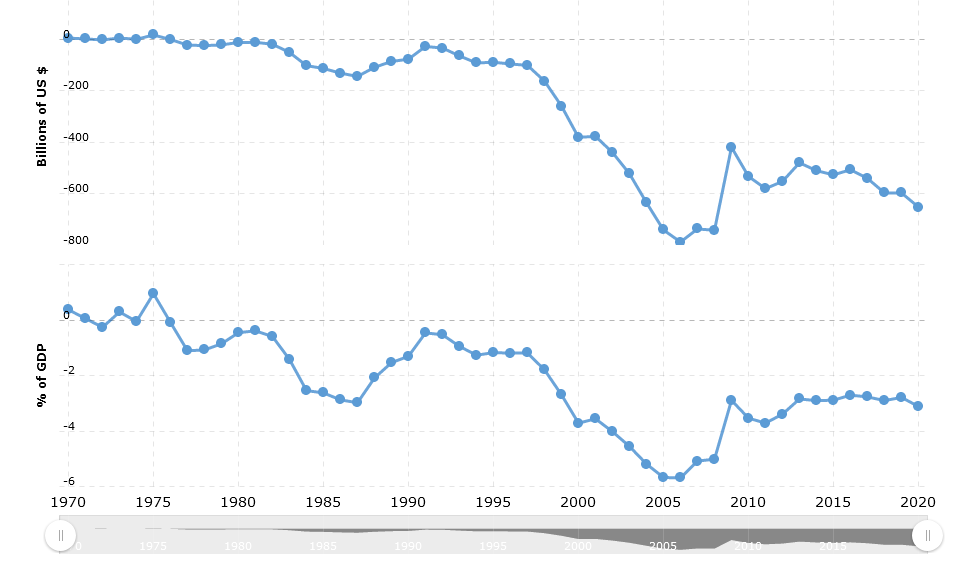
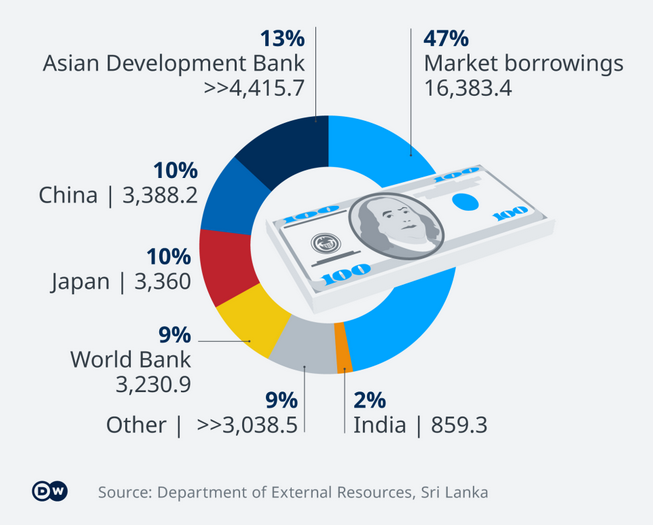
Eric Anderson wrote an excellent post on how late-stage capitalism engenders mental illness. I thought I’d follow it up with a simple post on capitalism.
As the name implies, capitalism is the accumulation of capital. This doesn’t mean money, primarily, that’s not what the early theorists meant by capital: they meant the means of production: land, workers, resources and capital goods: machinery in particular.
Capital is the ability to make and grow items. Because of economy of scale, if you concentrate capital it is easy to increase how much you make: Adam Smith’s famous pin factory.
But to concentrate capital you have to take it from a large number of people and put it in the hands of the few. This has been covered by a number of authors, and it involves taking away the commons rights of people in Europe (their right to use the land, which had existed for about a thousand years or so). We demonize serfs and peasants, and they had to engage in demeaning acts of servility, but they had strictly defined obligations to their lords for a certain amount of work, crops and animals and once that was taken care of they were able to spend their time as they pleased and they could grow crops on land they had right to; pasture their animals and so on.
Economists call the concentration of capital “primitive accumulation” but what it was was taking away property rights from people so they couldn’t support themselves. This forced them to go to cities and work in factories and so on, where they lived shorter lives, worked a hell of a lot harder (6 1/2 12 hour days were pretty common) and were sick a lot more often. The freedom of capitalism is the right to sell your labor, not the right to control how you spend your day. Unlike serfs and peasants, who were tied to the land, you could choose your master, but for most of the population, that’s what it was, a choice of masters, at least when there weren’t enough workers.
In the rest of the world European capitalism was about conquering land and into the 19th century, about taking slaves. The only thing better than workers who are desperate being workers who you didn’t even have to pay.
Capitalism, again, is about concentrating the means of production, capital, in the hands of the few. It is justified by the idea that concentrated capital is more effecient and therefore everyone has more. There’s a lot of arguments about whether that’s true and we now know, for example, that land clearances didn’t increase agricultural productivity much more than on communal lands, and in the case of some crops, communal lands were more efficient.
But it’s hard to make the case for the path not taken. Perhaps communal forms could have worked, I think they could have, and would have produced more prosperity in time, since they didn’t involve impoverishing people and two-thirds of the non-European globe, but… the water is passed and the argument is important not for what might have been, but for what might be in the future.
But all systems are made up of means and ends. Capitalism justifies removing the ability of most people to support themselves without working for others beyond what amounts to taxation by the violent authorities (that’s all governments. Don’t pay your taxes and eventually the big men with guns will show up, just like the knights did when a peasant didn’t meet his feudal contract.)
The means of capitalism in the modern world amount to “wage slavery,” something well understood by they yeoman farmers who were being forced off their land in the 1800s, and who seem to have coined the phase. You will have a master and if you can’t find one, you will starve.
It’s important to separate “capitalism” and “industrialization”. Because we industrialized under capitalism we think of the two as the same thing, or perhaps as co-joined siamese twins, but it’s not hard to imagine industrializing, which is about machines and assembly lines, in different ways: perhaps with communal organizations co-owning the means of production. This is distinct from Soviet communism, in which the government effectively owned everything, leading to the normal problems of totalitarian organization. Plurality and capitalism and synonyms.
This is something you need to think through; to imagine, for yourself. Try and come up with different ways industrialization and technology could have advanced, and don’t be caught up in historical inevitability. If you think that the past could not have been any different, then you effectively believe the future is determined.
This is one of the issues of Marxism: historical determinism. When it turned out (at least so far) that the historical dialectic didn’t work out how Marx and Engels envisaged, well, the house of cards collapsed. You have to give up inevitability to have choice and the ability to adapt.
We have plenty of options for the future and do not have to make the mistakes of the past. The first principle is that if your means are bad, no matter how good your ends, your society is going to have huge problems. You can’t routinely do evil, day in and day out, and expect the some invisible hand to lead to a good world for all.
The results of the work I do, like this article, are free, but food isn’t, so if you value my work, please DONATE or SUBSCRIBE.