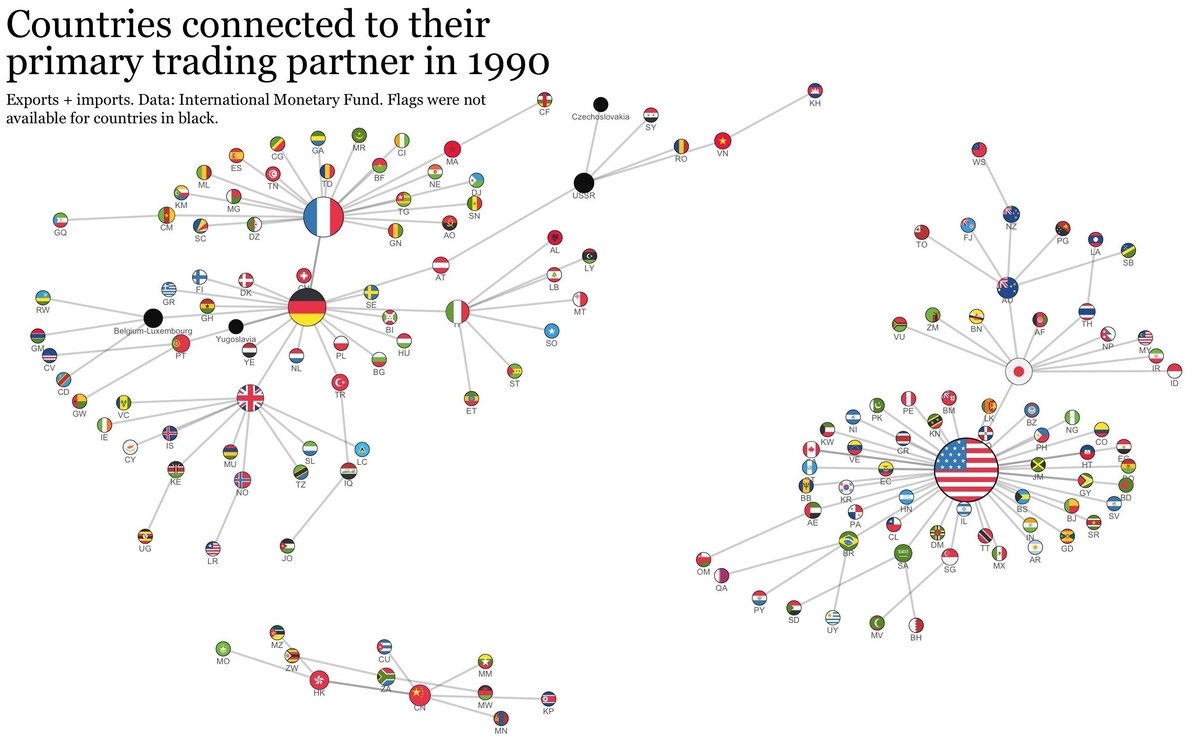
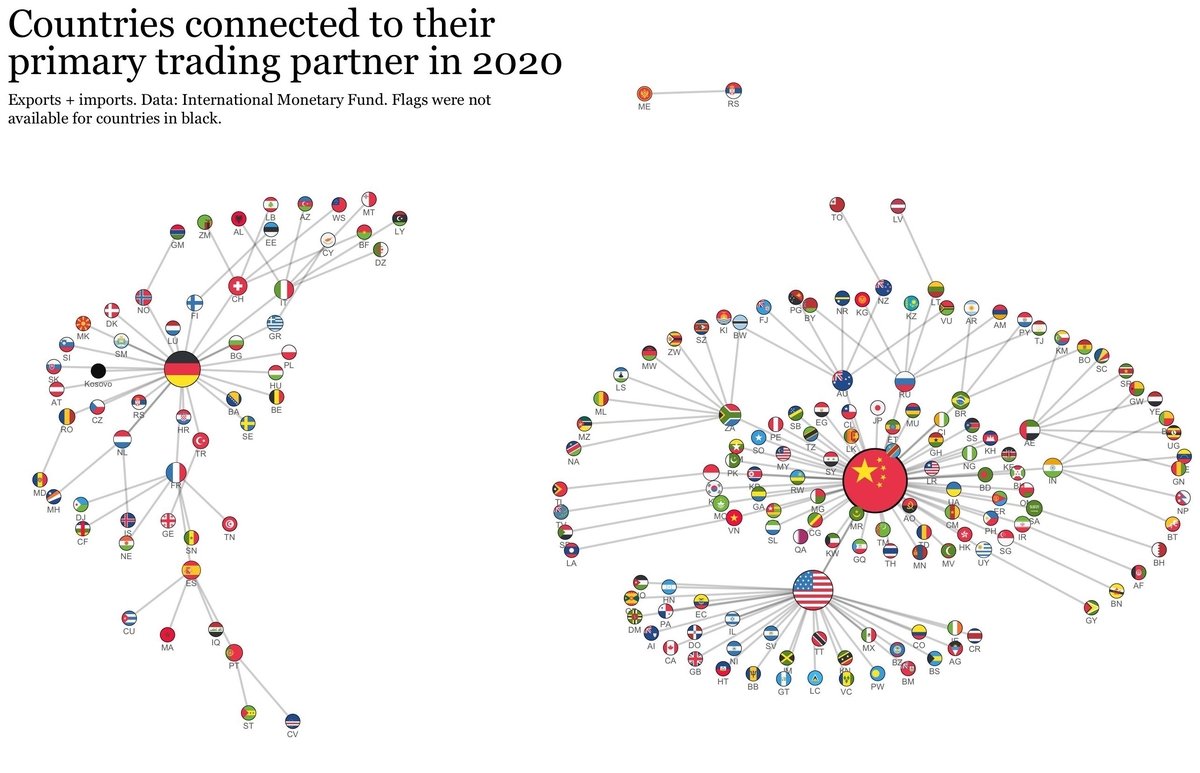
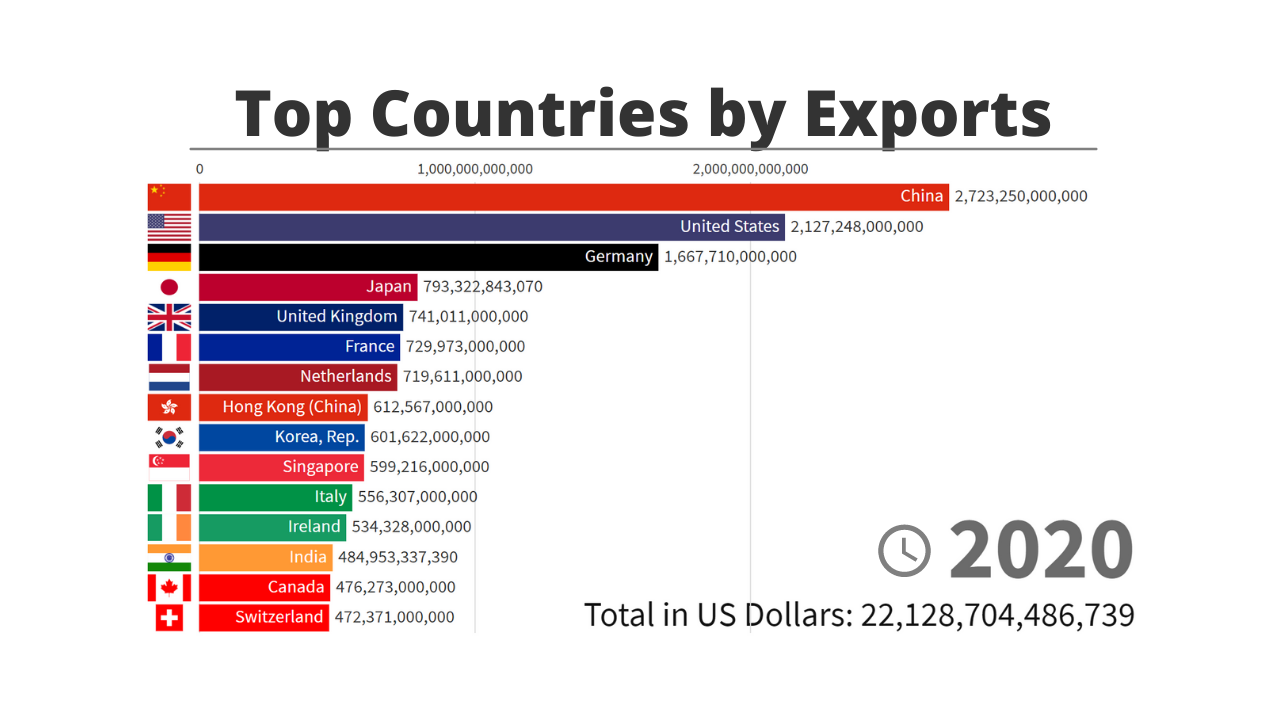
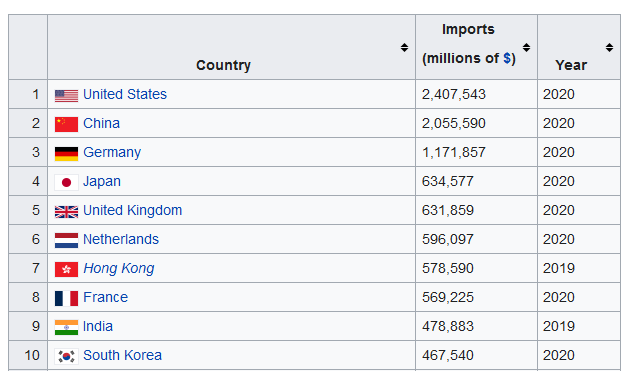
All right. Let’s talk some basic development stuff, primarily in the neoliberal era.
Because industrial policy was disallowed with a few marginal exceptions due to the “rule based order” enforced by a variety of trade agreements and organizations, the traditional route of protecting domestic industries and growing behind tariffs became very difficult to do.
Various countries used different dodges. Russia, to get out of the Yeltsin era collapse, went whole hog into resources: advanced nations had to have oil and natural gas and minerals, and bribed key financial regions like London’s city with huge influxes of resource-money.
China did something different. They opened up partially and let foreign companies in, but they used bureaucracy to keep them under control (as had Japan, in part) and offered foreign elites huge labor arbitrage profits. They bribed the West’s elites with personal wealth, in effect. In exchange they insisted on, generally very strictly, in real technology transfer. Meanwhile, they created a protectionist bubble thru monetary policy, keeping the exchange rate in their favor.
But the other thing they did is what Turkey tried. They created a self-reinforcing property bubble. Municipalities and states built tons of new homes, people flooded in from the countryside to get the new factory jobs and the service and government and construction jobs which supported industry. Prices went up, municipal and state budgets went way up and a virtuous cycle was created, for a time.
Turkey did the same thing, but the problem is Turkey didn’t have an expanding industrial base, and that’s why Turkey imploded sooner.
All bubbles, including property bubbles are time limited. The more of a real economy you have, the longer they can run, but eventually inflation in property becomes too high, and most citizens can’t afford the housing. Meanwhile, inflationary increases in living costs make workers too pricey, and the industrial base begins to suffer.
You can start from three positions.
- Like the US or UK or much of the EU you can start with an industrial base and cannibalize it, or..
- Like Turkey you can start with a poor but big country and cannibalize an increasing part of your population, plus what little industry and agriculture you have (India is similar, but much larger and managed to get some industrialization out of this strategy), or..
- Like China you can build your industrial base at the same time.
Whatever you do, this strategy eventually runs into the roadblock of a cost structure which becomes too high to allow actual productive industries.
At that point, you have to tame the housing market and other out of control costs (medical, food, whatever). If you don’t, you’re pushed back from 3 to 1, or if you did 2, the artificial prosperity begins to collapse. (India’s calories per capita have spent decades decreasing and someone who spent time there in the 80s, I can tell you Indians weren’t overfed to start with.)
So China’s now in a position where rather than bubbles, especially the housing bubble, being synergistic with industry and improvements in technology, they’re starting to strangle growth.
The route out (minus mercantalist imperialism, which is long run a loser too) requires you to stop relying on property bubbles, and start strangling your cost structure. The “free” money from asset bubbles has to go away, and you have to create a consumer society: not one like we have now, but one like we had in the post-war liberal era. Housing costs have to be kept at a level where people can buy or rent homes fairly easily: 30% of wages for rent or so, and at most about 5 years wages to buy a small home or condo.
Since the free profits of bubbles and speculation have to go away, companies have to make real money by providing real services and not just count on “real estate always goes up” or (America) “people have to have health care, so we’ll increase prices thru the roof.”
This is the task that China now has. It’s a hard task, akin to getting of hard drugs like heroin or SSRIs or Xanax. It hurts, because the financial pipes are reliant on what amounts to free or easy money.
During this transition, headline GDP and so on will suffer, there is no way around it minus looting expeditions, especially since simply running the printing press (something we’ll talk about in another article) defeats the point, which is making companies earn their money by providing goods and services for small markups at scale. (The post war liberal era worked on 3-4% markups for most mass goods.)
This is where China is. Where America and most of the West is similar: except it’s after destroying much of the industrial base and real consumer economy that doesn’t rely on massive price gouging on items people must have. There is no way to bring the good jobs back for most of the population in the US or UK or Canada or Australia without crushing the cost structure, strangling property speculation and prices and in the US tackling the medical and drug cartels.
China’s making the attempt. A lot of what they’re doing is clumsy and crude (but then, so was the one child law, but it worked even if it caused future problems.) So far the UK and Canada and the US and most of the West are not even trying, which is why you hear more about friend-shoring (aka to cheap places that are Western allies) rather than re-shoring, which can only be done for the goods that are either very high margin or which elites have realized are too militarily strategic to do in other countries.
This is why, as far as I’m concerned, the smart money is still on China, and if it wasn’t for climate change and ecological collapse, I’d consider it a done deal even if it took a couple more decades and a lot of screaming and shooting.
As it is, we’ll see. But China’s at least trying to do the right thing.