The poor will always be with us, or at least as long as Republicans are also with us:
Virginia’s Republican-run House of Delegates rejected a proposed expansion of unemployment benefits Wednesday, along with $125 million in federal stimulus cash to pay for it.
On a mostly party-line 46-53 vote, the House turned down amendments by Democratic Gov. Timothy M. Kaine that were necessary to make Virginia eligible for the federal aid.
Modern Republicanism laid bare: never help anyone who really needs help. But that’s not the worst of it, the abysmal economic illiteracy is:
“It is not stimulus. Paying workers not to work does not promote economic growth,“ Byron said.
Actually, Delegate Kathy Byron, paying workers not to work does promote economic growth. This is economics 101, people who have money (unless they’re useless rich) spend that money. When they spend that money they spend it on products and services made by people who work. The more of those products and services which are bought, the more economic growth there is, since you can’t have economic growth if there’s no demand for products and services.
In times when there is insufficient demand, like in a massive recession or depression, the best thing to do is for the government to spend. And since there are people losing their houses, who are going without food, clothes and medical services, the best way to spend is to give those people money so you kill two birds with one stone: you get demand through spending, and you help people who need it so they don’t wind up starving or on the street.
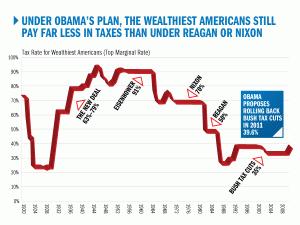
But let’s extend this even further—when you have a demand problem and you also have very high income inequality (money pooling with the rich, who tend not to spend it) an even better way to increase demand is to increase tax rates on the rich, and then spend that money. You could even give it to the poor and middle class, who haven’t had a raise in 30 years.
And yes, Byron, that would create economic growth, though I’m sure you aren’t capable of understanding that. But it worked for FDR, Truman, Eisenhower and so on, and it would work now, while the Reaganesque policies of the last thirty years haven’t worked and have led to this disaster.
So, if you actually care about economic growth (we won’t pretend you care about unemployed people) you should both accept the UI money and push for highly progressive taxation.
I won’t be holding my breath for you to understand any of this, Byron, but I will hope that eventually enough politicians will decide to stop trying the same failed Reaganite policies over and over again, and do something that works.
Eventually, after most of the current crop of legislators are unemployed themselves.
(h/t Not Larry Sabato)