Alright, let’s cover this again, with a bit more explication, since the idiots are really doubling down on “oh no, decreasing population.”
If you want to see it on a map, here goes:
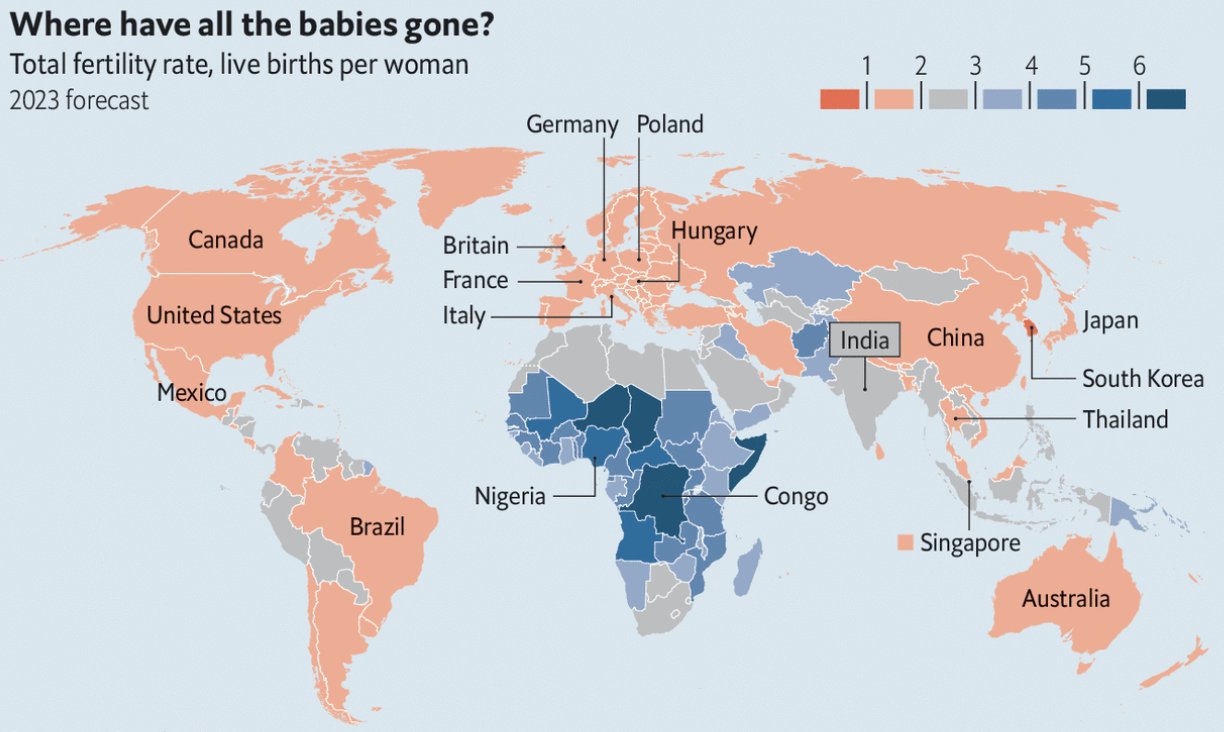
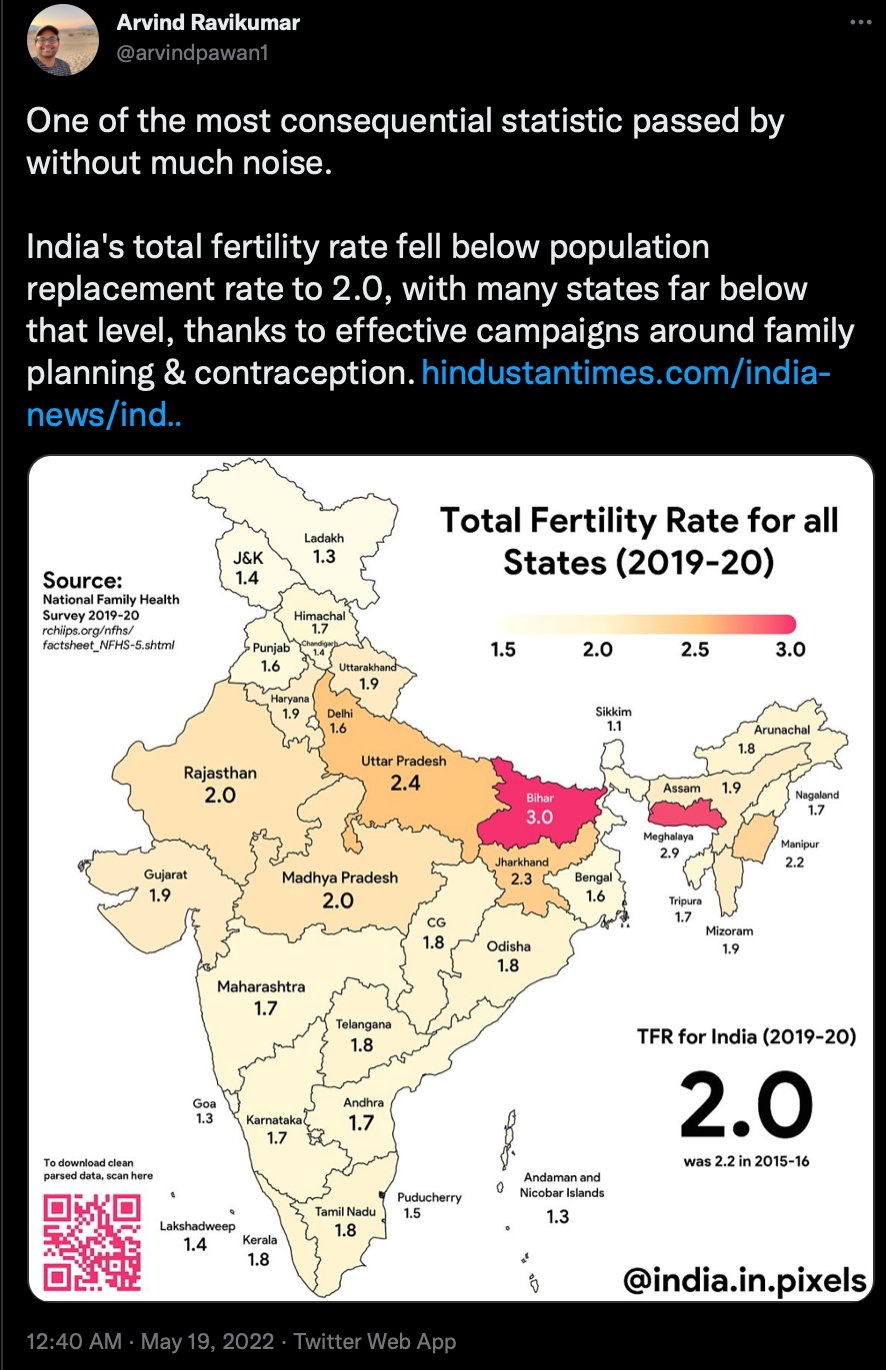
Even India has dropped to about replacement rate.
Now, let’s deal with this.
First, to the extent the plummet in birth rates is because of decreased biological fertility, like reduced sperm counts, it’s bad.
Second, despite this, we are well over the world’s carrying capacity and you are seeing it in the collapse of other life forms (ecological collapse) and climate change.
Third: the world’s carrying capacity is variable in a sense: what matters is number of people times the average per capita carrying cost of each person.
Fourth: the more population we want to have, the lower our per capita carrying costs have to be.
Fifth: a lot of people whine about this and to a certain extent rightly so. It is associated with austerity.
Sixth: imagine a world in which you bought a phone and used it for 20 years with modular upgrades; a car and used it for 50 (with modular upgrades); a washer and dryer and used it for 75 years, and where all of those things, when they finally ended their lives, were carefully recycled as much as possible.
Imagine a world in which almost nothing was made out of plastic. (In the 70s almost all bottles were glass and we used paper bags and grocery items were not individually wrapped in plastic and fuck “germs!” Covid has proven we don’t really care about that.)
Imagine a world in which we work half as much, create stuff that lasts for decades or even half a century or more.
Seventh: “but how can we afford this?” We can afford anything we can actually physically do. Each individual item would be more expensive, but last far longer and be cheaper overall. Yes, we would have to change how we distribute permission to have things, but we need to do that already.
Eighth: even in capitalist terms the “oh, without population gain how can we have economic growth” stuff is incoherent. Capitalism is supposed to increase productivity massively, so you should still be able to have growth, certainly per-capita growth. If you can’t, you’re a bad capitalist.
Ninth: that particular issue is related to oligarchs wanting to funnel all the money upwards and instead of relying on customers, rely on government, including central bank, subsidies. (Neither Tesla nor SpaceX would have made it without massive government subsidies.) In actual capitalism capitalists want high wages, because “everyone else’s employees are my customers.” The cost of high wages is more than made up for by people being able to afford their goods. This is why the economy of the post-war era was so good: high wages and lots of consumptiong.
Tenth: of course this sort of capitalism has to go away, we can’t afford a planned obsolesence economy in a world over carrying capacity and with limited stocks of key resources (the way we’re burning thru lithium should be literally criminal). But even in capitalist terms “oh no, population decrease” is an admission of failure.
Eleven: the dependency ratio is how many working people are supporting non-working (old, young, disabled and not allowed to work) people. Yes, a lower ratio makes things harder, but again, productivity is what matters and capitalism keeps claiming it’s good at raising productivity. Plus the actual percentage of people working for wages in high prosperity periods has often actually been lower than in high prosperity periods.
Twelve: oh, and worker compensation is likely to go up as population decreases and as the carry ratio decreases (or at least, be higher than it would have been otherwise, civilization collapse is also in the mix.) After the black death, welfare increased massively. We’re already seeing some of this effect due to the pandemic (one of the only good things to come out of it.)
***
We need less population. The world’s population has over doubled just in my lifetime (I’m 55). That’s ridiculous. And minus the internet and a few good medical improvements, I’ll tell you that life wasn’t worse then. (Even Africa had higher growth rates in the 50s and 60s and the dire poverty numbers are bullshit, because subsistence farming was far more common, but that’s another article.)
We have no problems we can’t adapt to, minus a few scenarios like the Venus runaway, a full ecological collapse which eliminates the apex species (that’s us) or polluting the world so much we can’t survive (which includes nuclear war.) We can, in theory and even in practice, if our politics wasn’t so screwed up, even make most people better off at the same time. But it will take time, and the most important problems are made simpler by population reductions.
What is going to make everything harder, actually, is our refusal to deal with Covid and our “New Emperor’s Clothes” insistence on pretending it’s over, while it continues as a mass disabling event. Yeah, we can handle a lower dependency ratio, but crippling hundreds of millions of people and making hundreds of millions more sicker is an unnecessary self-inflicted wound.
As before, as so far always in this crisis, the most important thing we have to do is replace our leadership class: political and private, en-masse, so that the correct decisions can be made. And yes, capitalism as we understand it is going to have to go away.
But this weird idea that population reduction right now is bad is breathtakingly stupid, and people who believe it have been fooled, or are fools
Folks, it’s your donations and subscriptions which make it possible for me to keep writing (since I need to eat and pay rent and the cost of both have skyrocked) so please (if you aren’t struggling) DONATE or SUBSCRIBE.


